If you’ve been wondering how exactly Liweli’s fast-acting CBD products work, here’s what it comes down to: your body’s endocannabinoid system, or ECS for short. The endocannabinoid system was only discovered by scientists in the 1990s, but it’s already become the focus of extensive research because of the indispensable role it plays in regulating day-to-day functions like sleep, mood, inflammation response, and appetite.
So, while your teacher may not have covered this regulatory system in 9th-grade biology, here’s the lowdown on what you should know.
H is for Homeostasis
Balance is important, balance is good. We often talk about finding balance in our lives, or maintaining a balanced diet, or even balancing our books. Homeostasis is the word used to describe that just-right balance that keeps our bodies functioning optimally. For example, body temperature shouldn’t be too hot or too cold, blood sugar (nor blood pressure) shouldn’t be too high or too low. This is the job of the ECS: to help promote communication and regulation on a cellular level so that we feel great, day and night.
Three Main Components
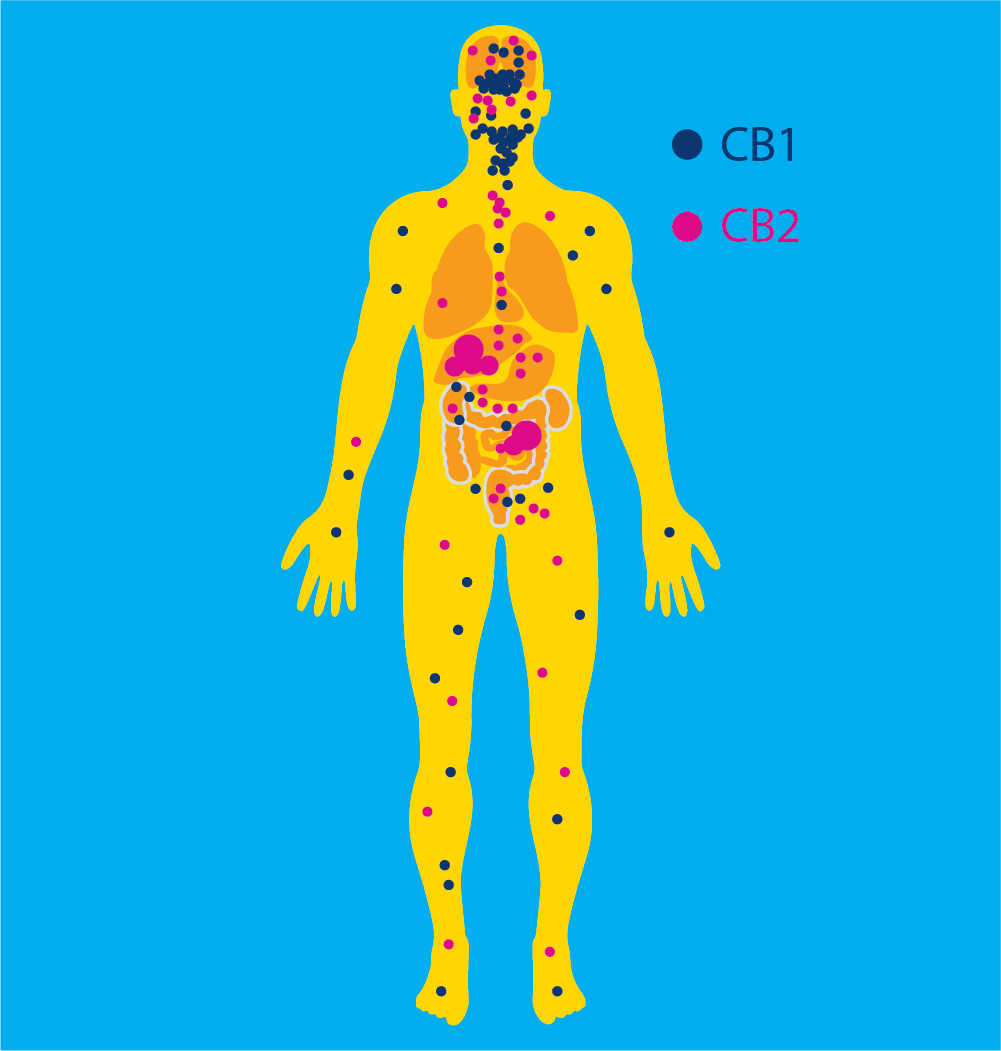
The ECS is an extensive network that stretches throughout the body. It’s made up of endocannabinoids, enzymes, and receptors that can be found in places like your spinal cord, brain, gut, and soft tissues. These components work together as a series of different locks and keys, which either trigger or block different actions on a cellular level. Your body naturally produces cannabinoids (those would be the “keys” to the “locks” that are the receptors, so to speak), which are called endocannabinoids. When you take CBD, you are adding plant-derived cannabinoids to the system, often called phytocannabinoids.
A Range of Reactions
Cannabinoids interact with different types of receptors in different ways, depending on the type and location in the body, allowing the ECS to act as a multi-purpose balancer. When some bodily function (pain response, for example) is not working optimally, endocannabinoid messengers tell receptors in the body’s cells to start powering it up. However, when there’s an over-active response, different combinations of endocannabinoid messengers and receptors can have those same cells lower levels back to a healthy range. It’s sort of like a ‘smart’ thermostat that knows exactly when to kick into gear to bring the house to that ideal pre-set temperature.
Vertebrates Unite!
It turns out humans are not the only living beings with an endocannabinoid system. It has been discovered that all animals, in fact, all vertebrates (refresher: that means all mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish) have an ECS. The oldest animal found to have cannabinoid receptors is the sea squirt, a barnacle-like animal that evolved 600 million years ago. So, there’s a strong biological basis for the therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids.